When I first got into the world of chromatography and laboratory work, the difference between vials and ampoules wasn’t all that clear to me. I mean, these are both tiny containers made of glass or plastic that hold liquids, right? But trust me, once you dive in, the nuances become pretty clear. Let’s chat about it, almost like we’re catching up over coffee.
The Basics of Vials and Ampoules
First, let’s break it down. What exactly are vials and ampoules? Both are small containers used in laboratories, pharmaceutical industries, and more. But, they’re not interchangeable.
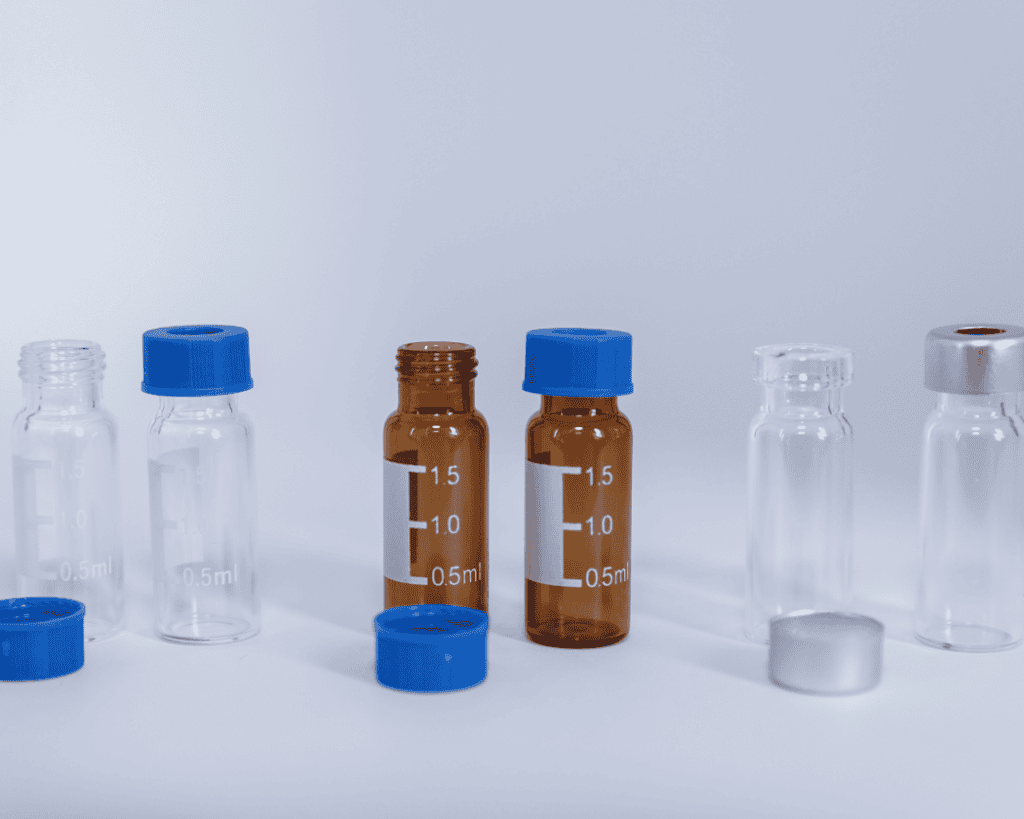

What is a Vial?
A vial is a small, cylindrical container typically used to store liquids, powders, or tablets. They’re commonly made of glass but can also come in durable plastics. Think of those tiny containers with screw tops, snap caps, or crimp seals—you might’ve seen them in medical kits or laboratories.
Vials are super versatile. They often have a broader opening, making them easier to access and refill multiple times. Do you know those little bottles with screw caps in your first aid kit or in labs? Those are vials! They’re designed for ease of use and reusability.
What is an Ampoule?
On the other hand, an ampoule is a completely sealed container, usually made of glass. Ampoules are specifically designed for storing sterile solutions or samples that need to be kept airtight and protected from contamination. They’re opened by snapping the neck of the glass—a little nerve-wracking, right? But that’s what keeps the contents safe.
Ampoules are mostly one-use items. They’re made for those times when you absolutely need to ensure the sterility and purity of a substance. Imagine a surgeon needing a pure saline solution—she’ll reach for an ampoule.
Key Differences Between Vials and Ampoules
While they may look similar at a glance, there are some clear distinctions that set these two apart. Let’s explore:
Seal and Sterility
One of the primary differences is how they’re sealed. Ampoules are completely sealed by melting the thin neck of the container. This process keeps the inside totally sterile until it’s time to break it open. It’s kind of like cracking open a glow stick, but with way more finesse.
Vials, on the other hand, can have various sealing methods—screw caps, crimp seals, and snap caps. They aren’t always sterile, but that’s not usually their purpose. What matters is their flexibility and reusability.
Reusability
Ampoules are generally one-use, period. Once you break that neck, there’s no going back! This design prevents contamination but also means you’ll need to dispose of the ampoule after it’s opened.
In contrast, vials can be used over and over again, as long as the sealing cap is in good condition. This makes them a go-to option when you need a reliable, multi-use container.


Applications of Vials and Ampoules
Now that we’ve looked at what makes them different, let’s see where each shines.
When to Use Vials
Vials are fantastic for storing solutions, powders, or any substance that you might need to access more than once. For example, if you’re in a lab setting working with chromatography, you’ll probably have vials for each sample. They’re easy to open and close securely, ensuring that your samples don’t spill or get contaminated.
What do I think of vials for chromatography? They’re essential. For HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography), having vials with high compatibility and durability is a must. That’s why investing in high-quality, lab-grade vials is crucial.
When to Use Ampoules
On the flip side, ampoules are the go-to choice when sterility is of the utmost importance. They’re used for injectable pharmaceuticals, sterile solutions, and sensitive compounds that need to remain untouched by outside air until the moment of use. Imagine needing to keep a sample perfectly pure for medical purposes; that’s where ampoules shine.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Just like with any tool, there are pros and cons to each. Let’s quickly weigh them out.
Advantages of Vials
- Reusable: Vials can be reused, which can help reduce costs.
- Versatile Sealing Options: From screw caps to snap lids, vials offer flexible sealing methods.
- Variety of Materials: You can find vials made from both glass and plastic, depending on your needs.
Disadvantages of Vials
- Not Always Sterile: Vials aren’t typically sterile unless you take steps to make them so.
- Potential Contamination: Because they’re reusable, there’s a risk of contamination if they aren’t properly handled.
Advantages of Ampoules
- Superior Sterility: Being sealed completely keeps ampoules free from contaminants.
- Ideal for Single-Dose: Ampoules are perfect when you need a precise, sterile dose.
Disadvantages of Ampoules
- Single-Use: Once an ampoule is opened, it can’t be sealed again.
- More Fragile: Being made of thin glass, ampoules can break more easily.
Conclusion: Which One Should You Choose?
So, which one is better? Well, it all depends on what you need. Vials are flexible and cost-effective, making them perfect for storing multiple-use substances in labs. But if sterility is your top priority, ampoules are the way to go. Personally, if I were running a lab that handled sensitive compounds, I’d stock up on both!
What do you think? Are you leaning towards vials or ampoules for your work?
Fianlly, if you’re on the lookout for high-quality HPLC vials at sensible pricing, you won’t miss out Mastelf. With over 13 years of experience in chromatography vials, we can help you find the exact vials you need for your applications.


Our expertise ensures that you get reliable and precise products tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you’re in pharmaceuticals, research, or any other industry relying on HPLC, we understand your needs and are here to support you in making the right purchase.
Reach out to Mastelf, and let us assist you in procuring the perfect vials for your work.