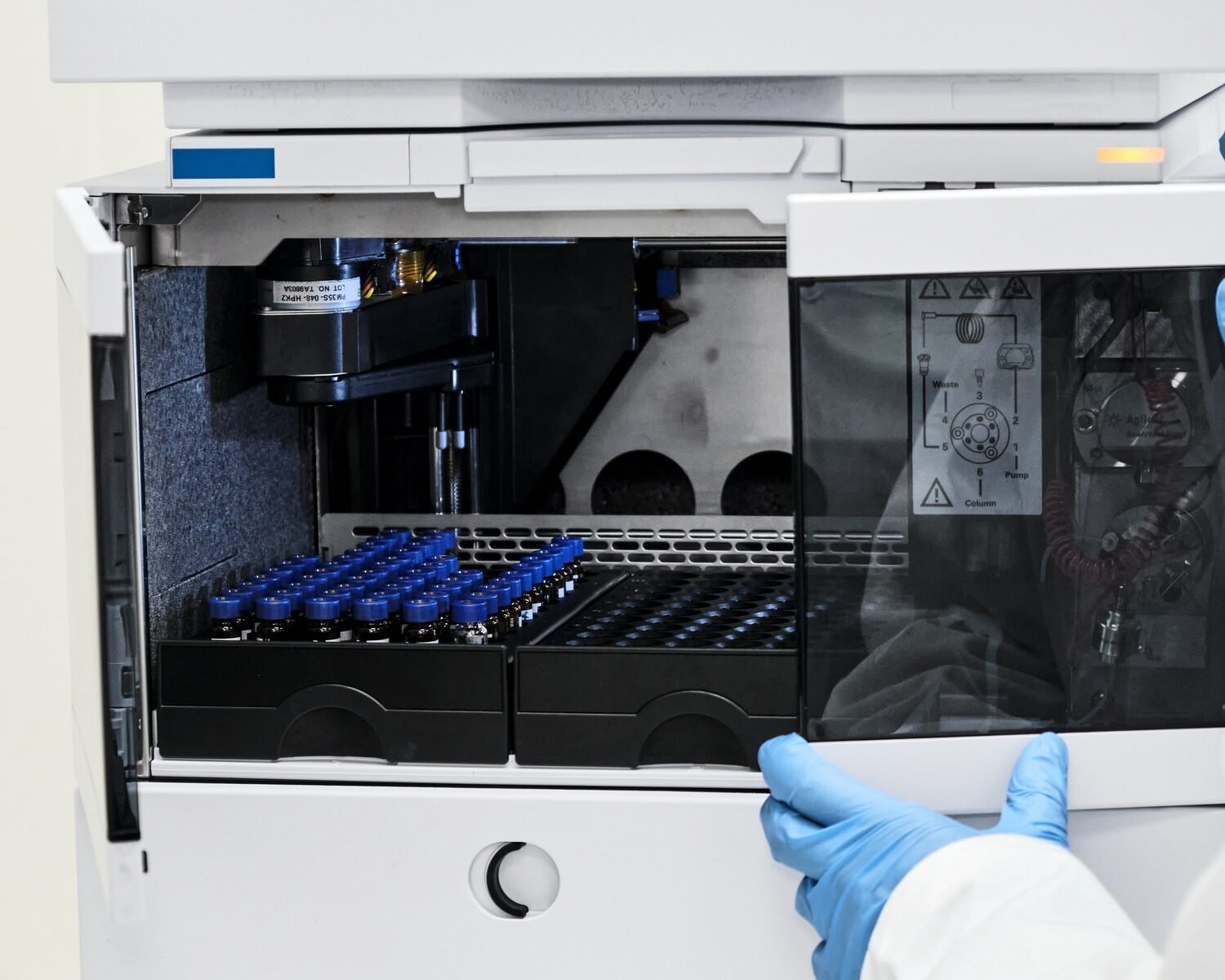
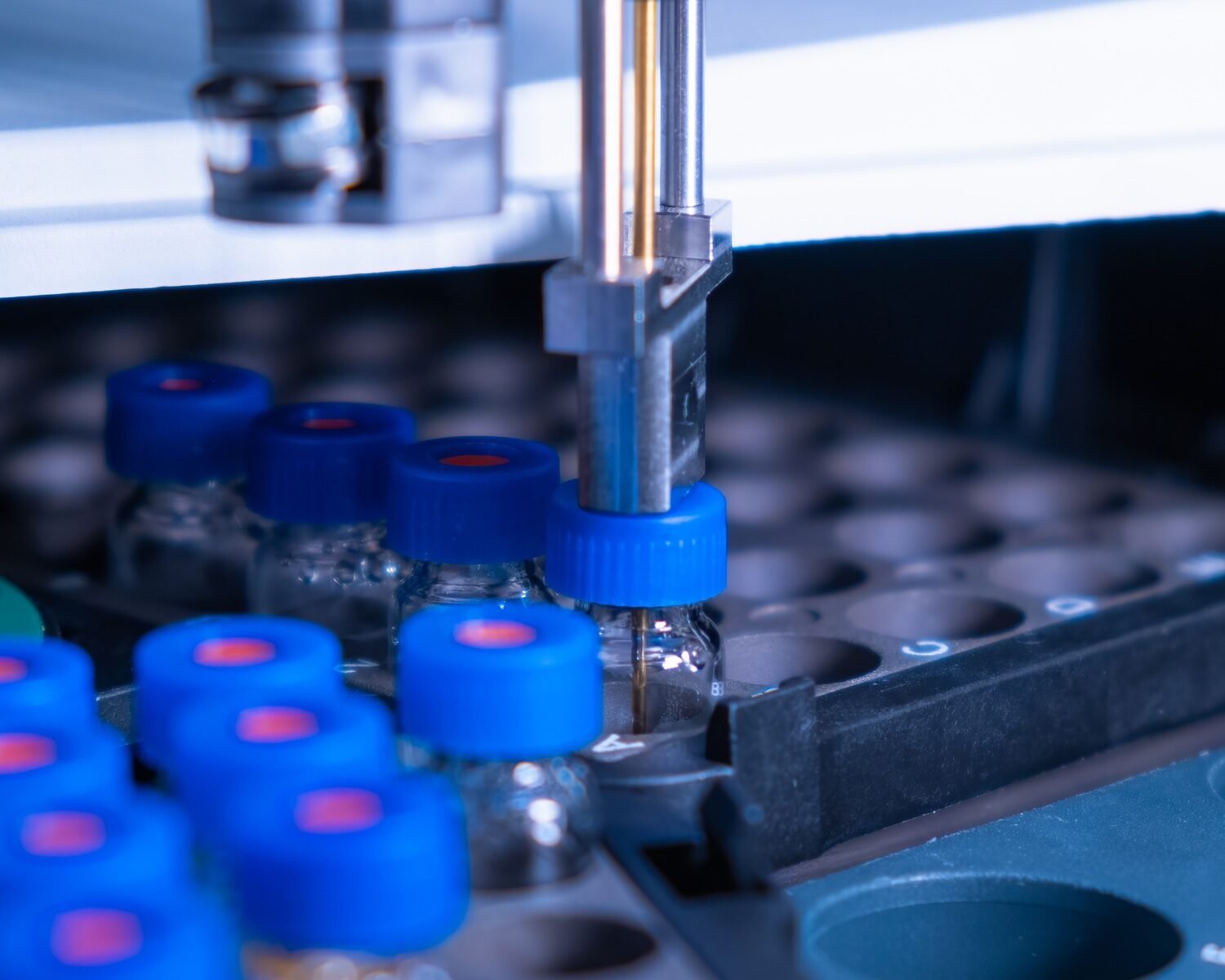
Introduction
When it comes to HPLC sample analysis, the storage of vials plays a crucial role in maintaining sample quality over time. Whether you’re dealing with volatile chemicals, biological samples, or sensitive compounds, improper storage can lead to degradation, contamination, or evaporation, ultimately compromising your results. Proper vial storage ensures that your samples remain stable, uncontaminated, and ready for accurate analysis.
In this guide, we’ll go over the top tips for vial storage and how to preserve your HPLC samples effectively.
Environmental Factors That Impact Vial Storag
When storing HPLC samples, the environment surrounding your vials can have a profound impact on their long-term stability. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key environmental factors that can affect your sample’s integrity.
- Temperature
Temperature fluctuations are one of the most significant risks when storing vials. Extreme heat can cause samples to evaporate or degrade, while excessive cold can cause crystallization or even rupture certain vials. It’s important to store samples at the temperature recommended by the manufacturer or the specific requirements of the sample type. For most compounds, room temperature or a refrigerated environment is sufficient. For sensitive samples, freezer storage may be necessary to prevent decomposition. - Humidity
Humidity can be a silent yet destructive force. Moisture can cause chemical reactions, lead to the hydrolysis of certain compounds, or degrade sealing materials. High humidity can also promote mold growth in biological samples, which would skew the results. To mitigate these risks, ensure that storage conditions are low-humidity and that vials are kept in sealed containers if required. - Light Exposure
Light-sensitive samples can degrade or undergo photochemical reactions when exposed to light. This is particularly relevant for samples containing organic compounds or biological molecules that are easily damaged by UV or visible light. Storing samples in dark or amber-colored vials, or in light-blocking containers, is the best way to prevent light-induced degradation.
Have you ever noticed any changes in your samples due to exposure to environmental factors? How did it affect your results?
Choosing the Right Storage Containers for Vials
Storage containers are essential for keeping vials organized, stable, and safe. Whether you’re dealing with glass vials, plastic vials, or specialized containers for sensitive compounds, the right container can significantly enhance your storage practices.
- Vial Racks
Vial racks are a practical way to keep vials upright and prevent them from tipping over or breaking. Look for adjustable racks that can accommodate various vial sizes. These racks also allow for easy access and organization in your laboratory, reducing the risk of contamination from improper handling. - Storage Boxes
Storage boxes are especially useful when storing vials in bulk or in freezers. They provide an extra layer of protection against freezer burn or potential damage from low temperatures. Foam inserts within the boxes can hold vials in place, preventing them from moving and ensuring stability. - Sealed Containers
If you’re working with volatile solvents or sensitive biological samples, sealed containers are essential for preventing contamination or evaporation. For these types of samples, airtight containers or vacuum-sealed boxes can ensure that your vials remain protected from external factors like air, moisture, and temperature changes. - Cryo Storage Vials
For long-term storage of samples that require cryopreservation, you should invest in cryogenic storage vials. These vials are specifically designed to withstand extreme cold temperatures and are made from materials that prevent freezer cracking.
Have you used any specific storage containers that you swear by? What kind of storage setup do you use for your samples?
Best Practices for Long-Term Sample Storage
When it comes to long-term storage, proper techniques and strategies are necessary to preserve the integrity of your samples. These best practices ensure that samples remain in a stable state, even if stored for extended periods.
- Short-Term Storage
For short-term storage (less than a few weeks), samples can typically be stored in standard vials at room temperature or in a refrigerator (4-8°C). Make sure the vial is tightly sealed, and check regularly for any signs of evaporation or contamination. Short-term storage is usually sufficient for routine analyses or experiments. - Long-Term Storage
For long-term storage, it’s crucial to freeze or deep-freeze your samples, especially if they’re prone to degradation at room temperature. Use cryogenic storage containers for samples that need to be stored at -80°C or lower. It’s also advisable to store samples in small aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles, which can degrade sensitive compounds. - Temperature Monitoring
For sensitive compounds, always monitor storage temperatures using a digital thermometer or a temperature data logger. This ensures that samples stay within their required temperature range and alerts you to any fluctuations that might compromise sample integrity.
Do you follow specific protocols for long-term sample storage? What has worked best for you in terms of keeping samples stable over time?
Minimizing Sample Degradation: Special Considerations for Sensitive Samples
Some HPLC samples require special attention to avoid degradation. Certain samples are more prone to chemical reactions or physical changes when exposed to certain conditions. Here’s how to minimize sample degradation:
- Volatile Compounds
Volatile samples, like organic solvents, can easily evaporate over time. To minimize this, store volatile samples in airtight containers or use vials with PTFE-lined septa to prevent loss through the seal. Always store such samples at low temperatures to slow down evaporation and chemical reactions. - Light-Sensitive Samples
Samples that are sensitive to light, such as certain vitamins or pharmaceutical compounds, should be stored in amber vials or lightproof containers. If light exposure is inevitable, limit the duration and intensity of exposure to avoid degradation. - Temperature-Sensitive Samples
Some samples degrade rapidly at higher temperatures, while others are stable only at sub-zero conditions. If you’re storing biological samples or pharmaceutical compounds, ensure you know the specific temperature requirements. Freezing or refrigerating samples may be necessary to preserve their integrity.
Have you encountered degradation problems in sensitive samples? How do you ensure they remain intact during storage?
Tracking and Labeling Vials for Efficient Storage
Labeling and tracking are key practices for ensuring that your samples are properly identified and easy to retrieve.
- Clear Labeling
Each vial should have a legible label containing crucial information such as the sample ID, date of collection, storage conditions (temperature), and the composition of the sample. Use waterproof labels or laser-etched vials to prevent fading over time. - Organizing Samples
An organized storage system can save time when retrieving vials. Create a logbook or digital inventory system that tracks sample locations, especially if you have a large volume of vials. Use barcode labels for quick identification and efficient tracking. - Consider Color-Coding
Color-coded vial caps or storage boxes can help you organize samples according to different categories (e.g., volatile vs. non-volatile, aqueous vs. organic). This minimizes the risk of mishandling or confusion during storage and retrieval.
How do you organize and track your samples? What labeling strategies have helped you avoid confusion or misplacement?
Conclusion
Proper vial storage is crucial for preserving the quality and integrity of HPLC samples. Whether you’re storing volatile chemicals, biological samples, or light-sensitive compounds, following best practices for temperature control, humidity management, and sample organization can significantly improve your analytical results. By understanding the unique needs of your samples and employing the right storage containers, you ensure that they remain in optimal condition for accurate analysis.
Mastelf, with over 13 years of experience in chromatography vials since 2011, we can help you find the exact vials you need for your applications.


Our expertise ensures that you get reliable and precise products tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you’re in pharmaceuticals, research, or any other industry relying on HPLC, we understand your needs and are here to support you in making the right purchase.
Reach out to Mastelf, and let us assist you in procuring the perfect vials for your work.
FAQ
- How do I prevent evaporation of volatile samples during storage?
Use airtight containers or PTFE-lined vial seals and store volatile samples at low temperatures to minimize evaporation. - Can I store samples in regular plastic containers?
Regular plastic containers may not provide adequate protection for sensitive samples. Use cryogenic vials or specialized storage containers depending on the sample requirements. - What is the best way to label vials for long-term storage?
Ensure labels are clear, durable, and include essential information. Waterproof labels or laser etching are best for long-term labeling. - Should I store vials in the dark to prevent degradation?
Yes, if your samples are light-sensitive, storing them in amber vials or lightproof containers is recommended to avoid degradation. - How can I track the temperature of my stored samples?
Use a temperature data logger or digital thermometer to monitor and record storage temperatures regularly.











