When you’re in the lab and trying to find the right cap for your chromatography vials, it might seem like a simple choice, right? After all, how different can caps really be? Well, when it comes to things like phenolic caps versus polypropylene (PP) or polyethylene (PE) caps, there are some subtle but very important differences that can make or break your results.
So, what should you consider before making the switch between phenolic and plastic caps?
In this article, we’ll dive into the benefits, drawbacks, and specific applications of both types, helping you choose the best one for your needs. Trust me, this isn’t just about keeping your vials sealed; it’s about ensuring your samples stay pristine and your analysis stays spot on. Let’s get into it!
What Are Phenolic, PP, and PE Caps?
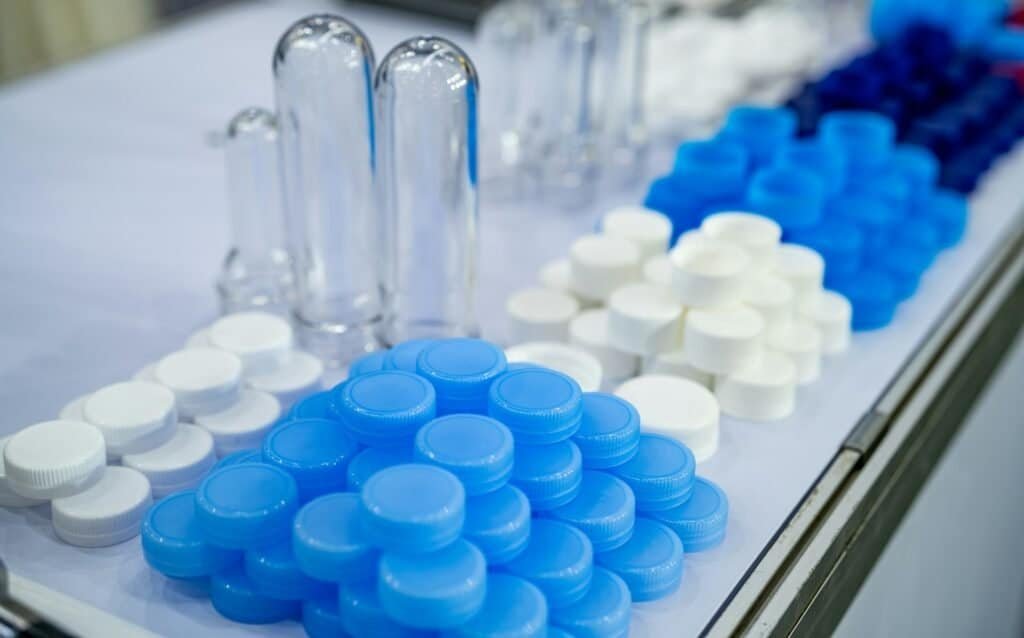

Before we get into the nuances, let’s break down what each of these materials really is.
Phenolic Caps
Phenolic caps, made from a thermosetting resin known as phenol formaldehyde (PF), are a classic choice in chromatography. These caps are often chosen for their chemical resistance, which is pretty impressive when you’re dealing with some of those highly reactive solvents and reagents in your lab. One major reason people opt for phenolic caps is their ability to withstand high temperatures. They don’t just melt under pressure, making them reliable for situations where heat might be involved.
But, here’s the kicker: Phenolic caps are rigid and more brittle compared to other materials. They also have a lower tolerance for extreme cold, and exposure to temperatures above 220°C can cause them to degrade.
Polypropylene (PP) Caps
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer known for its versatility. PP caps are cheaper, durable, and flexible, and, crucially, they’re autoclavable, meaning they can be sterilized without losing shape. This makes them an excellent choice for labs that prioritize cleanliness. They also have an impressive chemical resistance, although not quite at the level of phenolic caps when exposed to certain harsh chemicals. However, polypropylene caps are a better option if you’re working with lower temperatures.
They also have a decent temperature tolerance, with a melting point around 130°C, but if you’re planning to use them in environments that dip below freezing, you might want to look elsewhere. The material tends to become brittle at those low temperatures.
Polyethylene (PE) Caps
Polyethylene caps are somewhat similar to PP caps but generally are a bit softer and less rigid. They have a lower melting point (around 115–135°C), and they aren’t typically autoclavable. However, PE caps shine in situations where freezing is involved since they remain flexible at lower temperatures. While they aren’t as robust as PP or phenolic caps in terms of chemical resistance, they’re a great choice for more basic applications or for short-term sample storage in the freezer.
Pros and Cons of Phenolic Caps
So why might you choose phenolic caps? And, where do they fall short?
Advantages of Phenolic Caps
- Chemical Resistance: If your lab work involves aggressive chemicals, phenolic caps are an excellent choice. They’re known for their resilience against acids, bases, and solvents.
- Temperature Resistance: While they’re not perfect in freezing environments, phenolic caps perform well under high temperatures (up to 220°C) without deforming.
- Durability: Their rigid structure means they’ll last long, especially in tough conditions.
Disadvantages of Phenolic Caps
- Brittleness: They’re not the best for extreme cold. If you’re handling samples in freezing conditions, phenolic caps might crack or break.
- Limited Flexibility: While they’re tough in the heat, they don’t adapt well to varying conditions compared to polypropylene.
Pros and Cons of Polypropylene and Polyethylene Caps
Let’s turn our focus to the plastic options now. Both PP and PE caps are common, but which one should you choose?
Advantages of Polypropylene and Polyethylene Caps
- Autoclavable (PP): Polypropylene is autoclavable, making it a great option for labs that require sterilization.
- Low-Cost Option: When working on a budget, polypropylene and polyethylene caps are often more affordable than phenolic alternatives.
- Temperature Flexibility: Both materials have a better low-temperature tolerance compared to phenolic caps. Polyethylene is especially useful in the freezer.
- Chemical Resistance (PP): While PP caps might not match phenolic caps in extreme conditions, they still offer decent resistance to a broad range of chemicals.
Disadvantages of Polypropylene and Polyethylene Caps
- Lower High-Temperature Resistance: Polypropylene can only withstand heat up to about 130°C. Beyond that, it starts to lose its shape and function. Polyethylene is even less heat-resistant, making it unsuitable for high-temperature applications.
- Less Rigid (PE): PE caps are softer and less durable than PP caps or phenolic caps, so they’re not the best choice if you’re looking for something long-lasting under heavy conditions.
When to Use Phenolic Caps, and When Not To
Given all this, you might be asking, What do I think is the best use case for phenolic caps? Here’s my take: If you’re working with very harsh chemicals, or if your work involves high-temperature processes (without freezing involved), phenolic caps are the way to go. They’re tough, durable, and reliable in the right conditions. However, if you’re handling more temperature-sensitive samples or need something that will perform in the freezer, phenolic may not be the best fit.

When to Use PP or PE Caps
For the everyday laboratory environment, where you’re not dealing with extreme chemicals or temperatures, PP and PE caps should serve you well. If sterilization is key, PP is your best bet; it’s autoclavable and durable under moderate heat. On the other hand, if you’re dealing with lower temperatures and you’re storing samples in the freezer, PE might be your go-to cap. These caps are cheaper, flexible, and work well in simpler setups.
What to Consider for Your Lab
- Temperature Requirements: High temps? Go with phenolic. Low temps? PE might be your hero.
- Sterilization Needs: PP is the clear winner if you need something that can be sterilized in an autoclave.
- Chemical Resistance: If you’re handling highly reactive chemicals, phenolic caps have the edge.
Conclusion
In the end, the best cap material depends on your specific needs. It’s all about what works best with your environment and the types of materials you’re handling. When choosing between phenolic, PP, and PE caps, consider factors like temperature tolerance, chemical exposure, and your budget.
What do you think? Have you had experience with these caps in your lab? What do you usually reach for when you’re facing a challenging experiment? Let me know, and let’s keep the conversation going!
Mastelf, with over 13 years of experience in chromatography vials, we can help you find the exact vials you need for your applications.


Our expertise ensures that you get reliable and precise products tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you’re in pharmaceuticals, research, or any other industry relying on HPLC, we understand your needs and are here to support you in making the right purchase.
Reach out to Mastelf, and let us assist you in procuring the perfect vials for your work.